India’s Chandrayaan 3 mission aims to rectify the unsuccessful landing attempt on the moon’s surface in 2019. With renewed interest in lunar exploration, India seeks to join China as the only nations to achieve a successful spacecraft landing on the moon. This blog post provides key details about the mission, including the launch date, objectives, and India’s space exploration ambitions.

The Launch:
Chandrayaan 3 is scheduled for launch on Friday, July 14, at 5:05 a.m. Eastern time (2:35 p.m. local time). The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), India’s equivalent of NASA, will provide live coverage of the launch on its YouTube channel, starting at 4:30 a.m.
What is Chandrayaan 3?
Derived from Hindi, Chandrayaan translates to “moon craft.” Once launched, a propulsion module will propel the spacecraft out of Earth’s orbit, enabling it to enter the moon’s orbit. The spacecraft includes a lander and a rover, which will attempt a controlled landing in the moon’s south polar region. Scheduled for August 23 or 24, the landing will occur when the sun rises at the designated site, and the mission will last approximately two weeks. During this time, the solar-powered lander and rover will conduct various measurements related to temperature, seismic activity, and minerals.
The Chandrayaan-2 Experience:
Chandrayaan-3 represents a redo of part of the Chandrayaan-2 mission that encountered a setback in 2019. Although the mission successfully orbited the moon, the lander named Vikram and the rover named Pragyan experienced a trajectory deviation around 1.3 miles above the lunar surface, leading to a loss of contact with India’s mission controllers. The lander and rover were later discovered at the crash site with the assistance of imagery from a NASA orbiter.
India’s Moon Exploration Motivation:
India takes great pride in its space program, which serves as a symbol of national achievement. The success of the Mangalyaan spacecraft’s orbit insertion around Mars in 2014 further exemplified India’s capabilities and generated immense enthusiasm among its citizens. The exploration of the moon represents another step forward for India, boosting its growing cadre of commercial space start-ups. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has been closely involved in these missions, emphasizing the importance of effort and journey regardless of the final outcome.
Chandrayaan 3 mission modules
The primary components of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft are the lander module, propulsion module, and rover module. The propulsion module’s main purpose is to transport the spacecraft from an injection orbit around Earth to a lunar orbit located 100 kilometers above the moon’s surface. However, in addition to this crucial role, the propulsion module will also carry a payload designed to capture spectral and polarimetric measurements of Earth. These measurements will be taken from the vantage point of the lunar orbit, providing valuable data about our planet from a unique perspective in space.
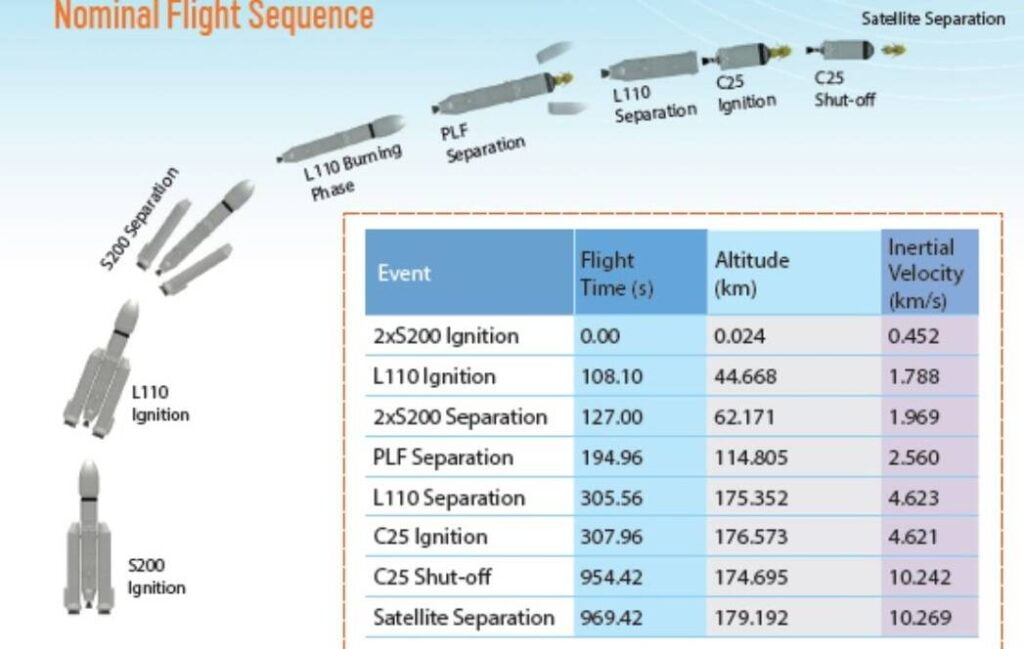
Future Plans:
In addition to Chandrayaan 3, India is actively developing the Gaganyaan spacecraft to carry astronauts into orbit, with an expected launch date no earlier than 2025. Furthermore, India is strengthening its collaboration with the United States for space missions. The White House recently announced that NASA will provide training for Indian astronauts, with a potential joint effort to the International Space Station in 2024.
Conclusion:
India’s Chandrayaan 3 mission represents the country’s determination to conquer the lunar surface after a previous setback. With the launch approaching, space enthusiasts worldwide eagerly anticipate the outcome and hope for a successful landing and exploration on the moon. India’s aspirations for space exploration continue to grow, fostering national pride and international collaboration in the pursuit of scientific discovery and technological advancements.
ALSO READ: https://usanewsdiaries.com/nothing-phone-2-review-come-to-the-bright-side/
